**CERT-UA Warns of UAC-0099 Phishing Attacks Targeting Ukraine's Defense Sector**
Ukraine's CERT-UA has issued a warning about phishing attacks by threat actor UAC-0099 targeting the country's defense sector, using malware such as MATCHBOIL, MATCHWOK, and DRAGSTARE. The National Cyber Incident, Cyber Attack, and Cyber Threat Response Team has investigated multiple attacks against state authorities, the Defense Forces, and enterprises of the defense-industrial complex.
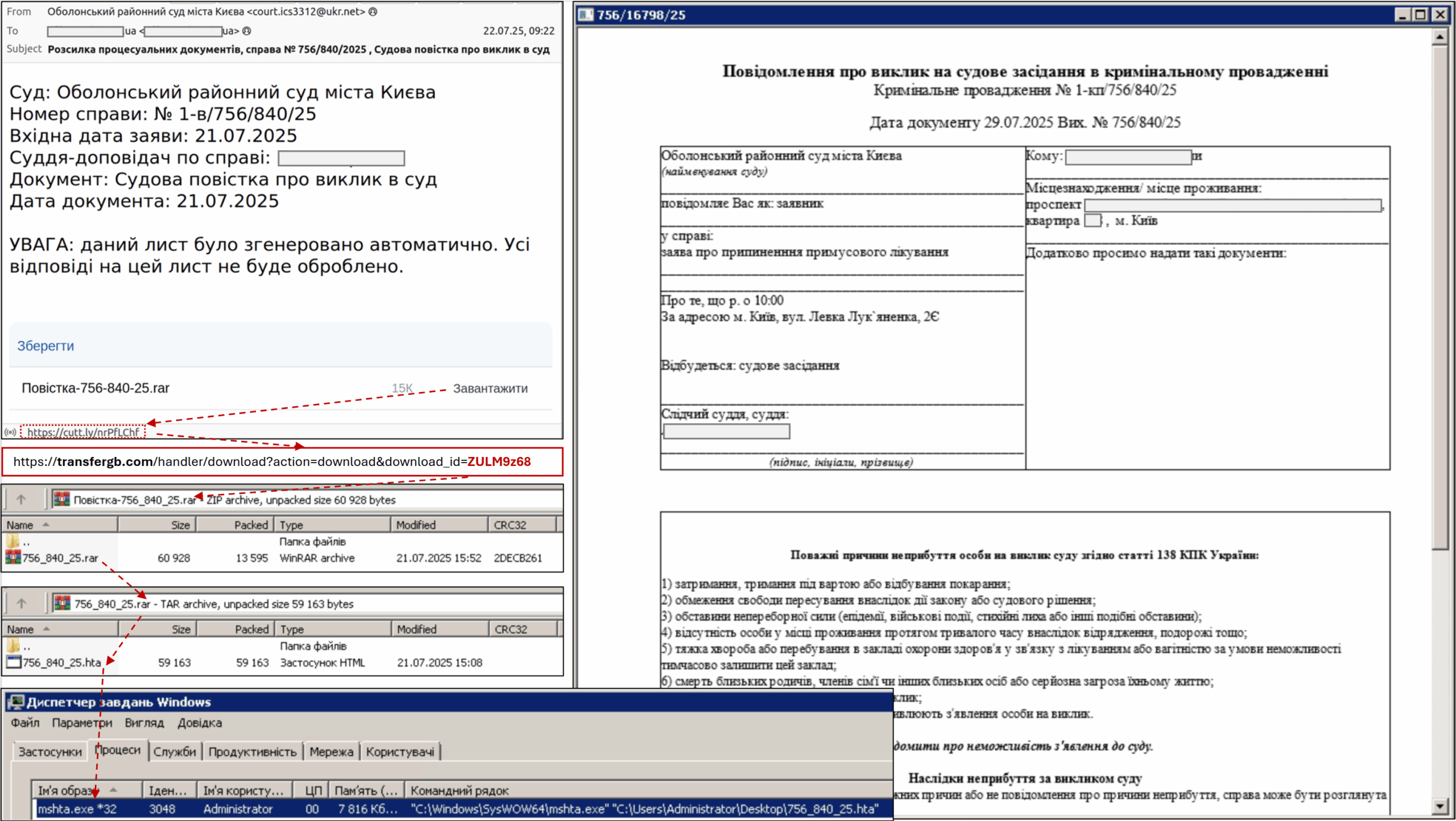
The attack chain begins with phishing emails, often titled "court summons," sent via UKR.NET. These messages contain links to legit file services hosting a double archive with an HTA file. When opened, the HTA runs obfuscated VBScript that drops files and creates a scheduled task to execute PowerShell code. This code decodes HEX data, writes it to a file, renames it to "AnimalUpdate.exe," and sets it to run regularly, activating the MATCHBOIL loader.
The attackers were also spotted deploying additional malware like the MATCHWOK backdoor and DRAGSTARE stealer. The researchers highlight the evolving tactics of the threat actors that demonstrate their persistence and sophistication.
**The Malware: A Closer Look**
MATCHBOIL is a C#-based loader designed to fetch and run additional payloads. It gathers system data (e.g., CPU ID, BIOS serial, username, and MAC address), which is combined and used in HTTP headers during communication with its C2 server. The malware downloads payloads hidden in image-like URIs, decodes them from HEX and BASE64, and saves them as ".com" files.
MATCHWOK is a C#-based backdoor that executes PowerShell commands by compiling .NET code at runtime, often using a renamed PowerShell executable. Command results are saved to a temp file and sent via HTTPS to a server whose address is read from a local config file. ATTACKERS USE THE MATCHBOIL LOADER TO MAINTAIN PERSISTENCE BY CREATING A REGISTRY KEY.
DRAGSTARE is a C# stealer that gathers system info, browser data (Chrome, Mozilla), and specific files (.docx, .pdf, etc.) from common folders. It steals login credentials, cookies, and archives found files for exfiltration. It also executes PowerShell commands from its server, evades virtual machines, and ensures persistence via a registry key.
**The Threat Actor: A Persistent Presence**
UAC-0099 has targeted Ukraine since mid-2022, and it was spotted targeting Ukrainian employees working for companies outside of Ukraine. In May 2023, CERT-UA warned of cyberespionage attacks carried out by UAC-0099 against state organizations and media representatives of Ukraine.
In December 2023, UAC-0099 targeted Ukraine by exploiting a high-severity WinRAR flaw CVE-2023-38831 to deliver the LONEPAGE malware. The threat actor's persistence and sophistication are evident in their evolving tactics, which demonstrate their ability to adapt and evade detection.
**Cyber Threat Indicators**
The report includes cyber threat indicators that highlight the risks associated with UAC-0099 attacks. These include:
* Phishing emails sent via UKR.NET * Use of HTA files attached to phishing emails * Malware such as MATCHBOIL, MATCHWOK, and DRAGSTARE * Scheduled tasks created by malware to execute PowerShell code * Stealing of login credentials, cookies, and archives
**Stay Safe Online**
To avoid falling victim to UAC-0099's phishing attacks, it is essential to stay informed about the latest threats and trends in cybersecurity. Stay vigilant and take necessary precautions to protect your devices and data.
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon